The complement system is a critical component of innate immunity, playing a pivotal role in host defense, immune surveillance and tissue homeostasis. Among
its key initiators, complement C1q is the recognition subunit of the C1 complex that triggers the classical complement pathway. The C1q C-chain (C1qC) is
one of three polypeptide chains (C1qA, C1qB, and C1qC) that make up the collagen-like and globular domains
of C1q. Recent research has highlighted the C1q C-chain as a promising drug target due to its involvement in autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative
disorders, cancer immune evasion, inflammatory and fibrotic conditions.
NCBI Gene ID: 714
UniProtKB ID: P02747
Structure and Function of C1QC
Molecular Composition of C1q
C1q is a hexameric protein (460 kDa) composed of:
-
Six heterotrimeric subunits, each containing A, B, and C chains encoded by C1QA, C1QB, and C1QC genes.
-
Collagen-like regions (CLRs): Mediate interactions with C1r/C1s proteases and cell
surface receptors, playing a key role in complement activation.
- Globular heads (gC1q domain): Recognize immune complexes, apoptotic cells, and pathogens, facilitating opsonization and clearance.
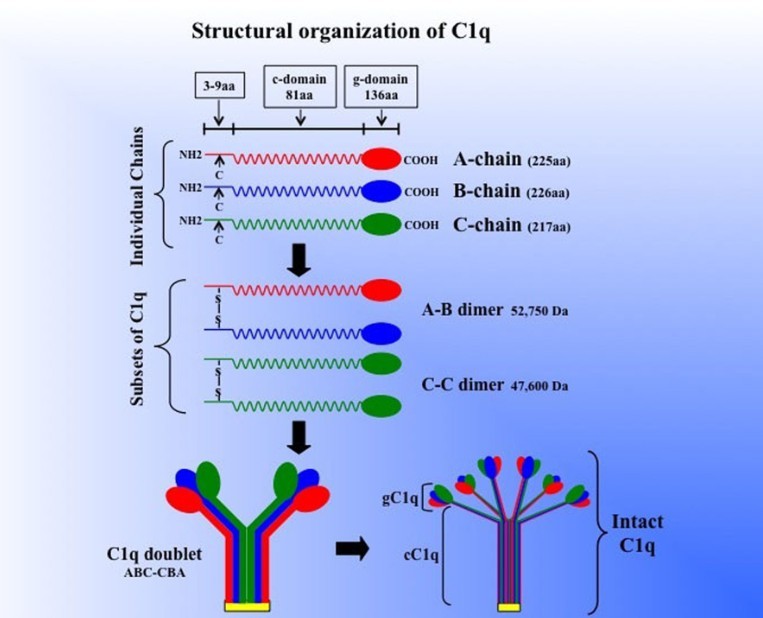 Figure 1. Schematic model of the subunit structure
and assembly of intact of C1q. Three similar chains – A, B, and C – are assembled to form disulfide-linked A–B and C–C dimers. One strand of the molecule
consists of an A–B dimer non-covalently linked to a C chain forming (A–B–C). The C chain of one strand is then disulfide-linked to the C chain of a
neighboring strand to give an A–B C–C B–A doublet and three such doublets are linked by non-covalent forces giving C1q its final signature "bouquet-like"
structure. The length of each chain as well as the length of the gC1q and cC1q domains (for brevity, g- or c-domain) is given in parenthesis. (Ghebrehiwet
et al., 2012)
Figure 1. Schematic model of the subunit structure
and assembly of intact of C1q. Three similar chains – A, B, and C – are assembled to form disulfide-linked A–B and C–C dimers. One strand of the molecule
consists of an A–B dimer non-covalently linked to a C chain forming (A–B–C). The C chain of one strand is then disulfide-linked to the C chain of a
neighboring strand to give an A–B C–C B–A doublet and three such doublets are linked by non-covalent forces giving C1q its final signature "bouquet-like"
structure. The length of each chain as well as the length of the gC1q and cC1q domains (for brevity, g- or c-domain) is given in parenthesis. (Ghebrehiwet
et al., 2012)
The C1q C-chain (C1qC) contributes to:
- Structural stability of the C1 complex, ensuring proper assembly and function.
-
Ligand binding, interacting with immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM), pentraxins (CRP, SAP), and β-amyloid, highlighting its role in both immunity and
neurodegeneration.
- Signal transduction, engaging receptors such as cC1qR (CD93), gC1qR, and CR1 (CD35), which modulate immune cell activation and inflammation.
Role in Complement Activation
C1q binding to immune complexes induces conformational changes, activating C1r and C1s serine proteases,
leading to:
- C4 and C2 cleavage → Formation of C3 convertase (C4b2a), amplifying the complement cascade.
- Opsonization, promoting phagocytosis of pathogens and apoptotic debris by immune cells.
- Inflammation, through the release of anaphylatoxins (C3a, C5a), recruiting immune cells to sites of infection or injury.
- Membrane attack complex (MAC) formation, leading to pathogen lysis and clearance.
- Clearance of apoptotic cells and immune complexes, preventing autoimmune responses by ensuring efficient removal of cellular debris.
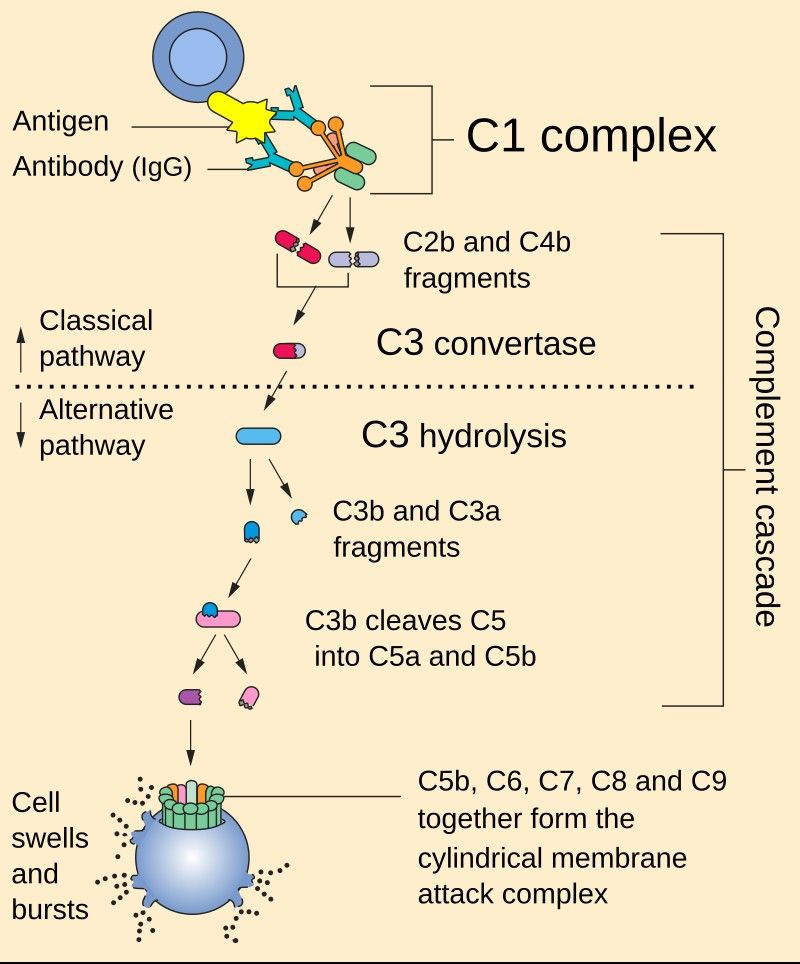 Figure 2. The classical and alternative complement
pathways. C1q is the orange part of the C1 complex at the top of the image.
Figure 2. The classical and alternative complement
pathways. C1q is the orange part of the C1 complex at the top of the image.
C1QC in Disease Pathogenesis
The C1q C-chain plays a critical role in immune modulation and its dysregulation has been implicated in several diseases, including autoimmune disorders,
neurodegenerative diseases, cancer progression and fibrotic diseases. Dysfunctional C1q activity can either exacerbate pathological inflammation or
contribute to immune evasion, making it a critical target for therapeutic intervention.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases arise when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, and C1q dysregulation has been associated with several such
conditions.
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): Defective C1q function impairs the clearance of apoptotic cells, leading to the accumulation of
cellular debris that triggers an autoimmune response. This failure of immune clearance promotes the production of autoantibodies against nuclear
components, exacerbating systemic inflammation. In addition, the presence of anti-C1q autoantibodies has been strongly correlated with the severity of
lupus nephritis, suggesting their potential as biomarkers of disease progression.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): In the context of RA, C1q deficiency results in inefficient clearance of immune complexes, leading to
persistent activation of inflammatory pathways within the synovial joints. This exacerbates joint inflammation and contributes to the chronic pain and
tissue damage characteristic of RA.
Neurodegenerative Disorders
Neurodegenerative diseases often involve aberrant immune responses in the central nervous system, where C1q plays a dual role in both neuroprotection and
neuroinflammation.
-
Alzheimer's Disease (AD): C1q has been shown to bind to β-amyloid plaques in the brains of Alzheimer's patients, facilitating
neuroinflammation by activating microglia, the brain's resident immune cells. This activation leads to excessive synaptic pruning and neuronal loss,
accelerating cognitive decline. Notably, preclinical studies have shown that C1q inhibition can reduce synapse loss and slow disease progression,
highlighting its therapeutic potential.
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): In MS, C1q contributes to disease pathology by promoting demyelination, a process in which microglia increase
phagocytosis of the myelin sheaths surrounding neurons. This destruction of myelin disrupts neuronal signaling and exacerbates neurodegeneration,
leading to progressive disability in affected individuals.
Cancer and Immune Evasion
Cancer cells exploit various immune mechanisms to evade detection and destruction, and C1q plays a significant role in modulating tumor immune responses.
-
Tumor cells have been shown to overexpress gC1qR, a receptor that interacts with C1q to suppress T-cell activation and promote an immunosuppressive
microenvironment. This allows tumors to evade immune surveillance and continue to proliferate unchecked.
-
C1q also contributes to tumor progression by promoting angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation that supplies nutrients to the growing
tumor mass.
-
Recent studies suggest that blocking C1q can enhance the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitor therapies, such as anti-PD-1 treatment, by restoring T-cell
function and improving anti-tumor immunity.
Fibrosis and Inflammatory Conditions
Chronic inflammation often leads to fibrosis, a pathological process characterized by excessive tissue scarring due to overactivation of fibroblasts.
-
Pulmonary and Renal Fibrosis: C1q has been implicated in fibrosis by promoting fibroblast activation and collagen deposition in
affected tissues. This contributes to progressive organ dysfunction in diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic kidney disease.
-
Scleroderma: Targeting C1qC has been shown to reduce collagen accumulation in experimental models of scleroderma, suggesting a
potential therapeutic strategy to mitigate fibrosis-related complications.
Therapeutic Targeting Strategies
Given the pathological roles of C1q in various diseases, several therapeutic approaches have been developed to inhibit its function and mitigate disease
progression.
Monoclonal Antibodies Against C1q
Monoclonal antibodies targeting C1q have emerged as promising strategies for treating autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders by blocking complement
activation.
Mirococept is a recombinant C1q inhibitor designed to prevent
ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplants, Mirococept acts by limiting complement activation, thereby reducing tissue damage and improving graft
survival.
Peptide Inhibitors
Peptide-based therapeutics offer another avenue for modulating C1q activity by disrupting complement activation and immune signaling pathways.
-
C1q-targeting peptides: These molecules, including C1q-binding aptamers, function by preventing C1q from initiating the classical
complement cascade, thereby reducing excessive inflammation in conditions such as autoimmune diseases.
-
gC1qR-derived peptides: Derived from the gC1qR receptor, these peptides have demonstrated the ability to suppress tumor growth in
melanoma models by interfering with C1q-mediated immune suppression.
Challenges and Future Directions
-
Safety and Selectivity
- Systemic C1q inhibition may increase infection risk (e.g., impaired pathogen clearance).
- Tissue-specific delivery (nanoparticles, AAV vectors) could enhance precision.
-
Biomarker Development
- Anti-C1q antibodies as prognostic markers in SLE.
- C1q plasma levels predicting response to complement-targeted therapies.
-
Combination Therapies
- C1q inhibitors + anti-PD-1 for cancer immunotherapy.
- C1q blockade + anti-TNF in autoimmune diseases.
Creative BioMart specializes in providing therapeutic proteins, contact us with any questions or inquiries.
References
-
Ghebrehiwet B, Hosszu KK, Valentino A, Peerschke EIB. The c1q family of proteins: insights into the emerging non-traditional functions.
Front Immun. 2012;3. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00052
-
Kishore U, Thielens NM, Gaboriaud C, eds. State-of-the-Art Research on C1q and the Classical Complement Pathway. Frontiers Media SA; 2016.
doi:10.3389/978-2-88945-058-9
 Figure 1. Schematic model of the subunit structure
and assembly of intact of C1q. Three similar chains – A, B, and C – are assembled to form disulfide-linked A–B and C–C dimers. One strand of the molecule
consists of an A–B dimer non-covalently linked to a C chain forming (A–B–C). The C chain of one strand is then disulfide-linked to the C chain of a
neighboring strand to give an A–B C–C B–A doublet and three such doublets are linked by non-covalent forces giving C1q its final signature "bouquet-like"
structure. The length of each chain as well as the length of the gC1q and cC1q domains (for brevity, g- or c-domain) is given in parenthesis. (Ghebrehiwet
et al., 2012)
Figure 1. Schematic model of the subunit structure
and assembly of intact of C1q. Three similar chains – A, B, and C – are assembled to form disulfide-linked A–B and C–C dimers. One strand of the molecule
consists of an A–B dimer non-covalently linked to a C chain forming (A–B–C). The C chain of one strand is then disulfide-linked to the C chain of a
neighboring strand to give an A–B C–C B–A doublet and three such doublets are linked by non-covalent forces giving C1q its final signature "bouquet-like"
structure. The length of each chain as well as the length of the gC1q and cC1q domains (for brevity, g- or c-domain) is given in parenthesis. (Ghebrehiwet
et al., 2012)
 Figure 2. The classical and alternative complement
pathways. C1q is the orange part of the C1 complex at the top of the image.
Figure 2. The classical and alternative complement
pathways. C1q is the orange part of the C1 complex at the top of the image.