| Catalog# | Product Name | Size | Price | Qty | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THP-0112 | Etanercept, Recombinant human TNFR, Fc tagged | 1mg | $1,298.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order |
| 10mg | $3,998.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order | ||
| THP-0152 | Alefacept, Recombinant human LFA3 protein, Fc tagged | 1 vial | $3,998.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order |
Complement C1q A chain (C1QA) is a subunit of C1q, the first component of the classical complement pathway, which is critical for the immune system's ability to recognize and clear pathogens, apoptotic cells, and immune complexes. C1q is a hexameric molecule consisting of three chains: A, B, and C, each encoded by a different gene. The A chain, encoded by the C1QA gene, plays a critical role in assembling the C1q complex and facilitating its biological functions. Structurally, C1q interacts with antibodies (IgG or IgM) bound to antigens, triggering a cascade of complement activation that leads to immune responses, including opsonization, inflammation, and cell lysis.
C1QA is primarily expressed in immune cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells. Beyond its classical immune functions, emerging evidence highlights its roles in tissue repair, apoptosis, and the regulation of inflammation, making it a key player in immune homeostasis.
NCBI Gene ID: 712
UniProtKB ID: P02745
C1QA and the classical complement pathway are involved in maintaining immune homeostasis. However, dysregulation of C1QA activity can shift the balance between protection and inflammation, leading to pathological conditions. C1QA's ability to mediate both beneficial and harmful immune responses makes it an attractive therapeutic target, particularly for diseases in which complement overactivation or dysregulation plays a central role. Below are key areas where targeting C1QA may have therapeutic benefits:
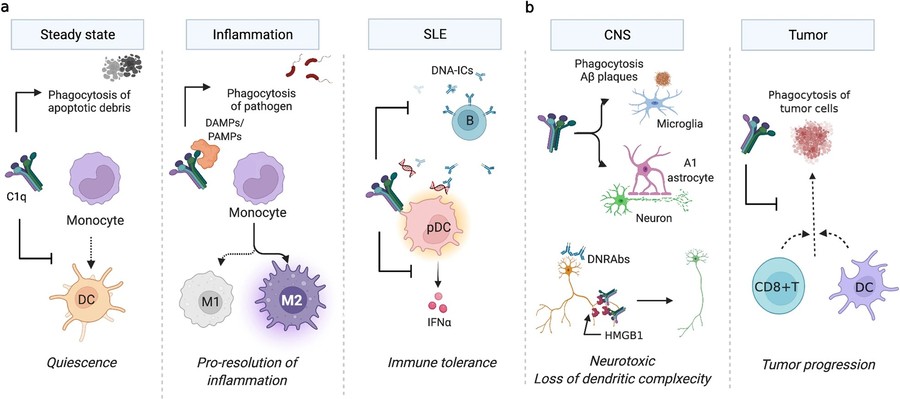 Figure 1. a C1q activates the classical complement
pathway and induces phagocytosis, allowing apoptotic debris clearance. C1q also maintains quiescence by inhibiting antigen-presenting DC differentiation,
which induces adaptive immunity. In the presence of DAMPs or PAMPs, such as HMGB1, C1q not only inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production but also
promotes anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophage polarization that is critical for the resolution of inflammation. Once SLE develops, C1q suppresses
DNA-containing immune complex (IC)-mediated pDC activation. b In contrast, in neuroinflammation or tumors, C1q promotes disease progression. In amyloid β
plaques in AD or neuroinflammation, C1q promotes A1 astrocytes and activates microglia that degrade neurons. C1q and HMGB1 promote the loss of dendritic
complexity and cognitive impairment. C1q inhibits CD8 + T cells and DCs that kill tumor cells. (Son, 2022)
Figure 1. a C1q activates the classical complement
pathway and induces phagocytosis, allowing apoptotic debris clearance. C1q also maintains quiescence by inhibiting antigen-presenting DC differentiation,
which induces adaptive immunity. In the presence of DAMPs or PAMPs, such as HMGB1, C1q not only inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production but also
promotes anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophage polarization that is critical for the resolution of inflammation. Once SLE develops, C1q suppresses
DNA-containing immune complex (IC)-mediated pDC activation. b In contrast, in neuroinflammation or tumors, C1q promotes disease progression. In amyloid β
plaques in AD or neuroinflammation, C1q promotes A1 astrocytes and activates microglia that degrade neurons. C1q and HMGB1 promote the loss of dendritic
complexity and cognitive impairment. C1q inhibits CD8 + T cells and DCs that kill tumor cells. (Son, 2022)
Direct inhibitors of C1q, such as monoclonal antibodies or small-molecule inhibitors, are being explored to block complement activation at the initial stage of the classical pathway. These therapies may prevent C1 complex formation and downstream inflammatory effects while preserving other complement pathways, such as the alternative and lectin pathways, which are essential for innate immunity.
Therapies aimed at reducing C1QA gene expression may provide a systemic approach to limiting C1q production in diseases where it is overexpressed. This can be achieved through techniques such as RNA interference (RNAi) or antisense oligonucleotides. Such approaches may offer long-term benefits in chronic diseases such as SLE, where persistent overactivation of C1q contributes to disease progression.
C1q exerts its function by binding to targets such as immunoglobulin complexes, apoptotic cells, or damaged tissues. Therapeutics that disrupt these interactions can provide selective modulation of C1q activity without affecting its synthesis or other immune functions. For example, peptides or small molecules that inhibit the binding of C1q to IgG/IgM could effectively prevent excessive complement activation in autoimmune diseases or ischemia-reperfusion injuries.
At Creative BioMart, we provide high-quality therapeutic proteins like etanercept. Contact us with any questions or inquiries.
References
For more information on how our products could help advance your project, please contact us.
ENTER YOUR EMAIL HERE TO SUBSCRIBE.
Copyright © 2026 Creative BioMart. All Rights Reserved.