| Catalog# | Product Name | Size | Price | Qty | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THP-0020 | Tenecteplase; Modified Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) | 100ug | $798.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order |
| 500ug | $2,498.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order | ||
| 1mg | $3,998.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order | ||
C-type lectin domain family 3 member B (CLEC3B), also known as tetranectin, is a soluble C-type lectin involved in extracellular matrix remodeling, fibrinolysis and immune modulation. Given its role in cancer progression, tissue remodeling and immune regulation, CLEC3B has emerged as a potential drug target.
NCBI Gene ID: 7123
UniProtKB ID: P05452
CLEC3B is a 20-25 kDa glycoprotein secreted primarily by hepatocytes and various connective tissue cells. Structurally, it contains a single C-type lectin-like domain (CTLD) that binds to plasminogen and promotes its activation to plasmin, a key enzyme in fibrinolysis. Unlike classical C-type lectins, CLEC3B does not primarily function in carbohydrate recognition, but rather interacts with protein ligands such as plasminogen and fibrinogen.
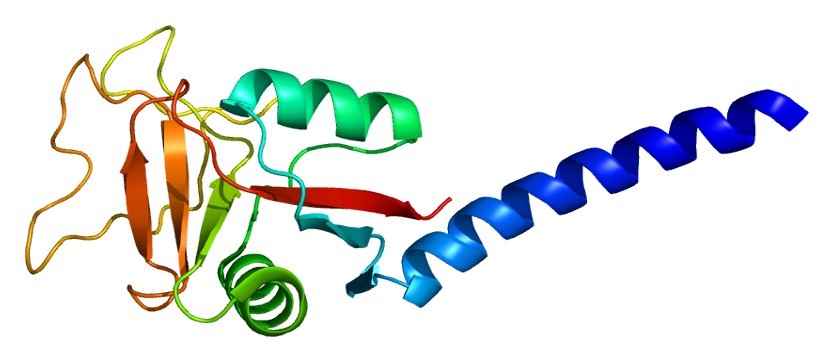 Figure 1. Structure of the CLEC3B protein, PDB
code: 1HTN.
Figure 1. Structure of the CLEC3B protein, PDB
code: 1HTN.
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for reliable biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis. CLEC3B has been implicated in several cancers, but its role in lung cancer remains unclear.
To investigate the significance of CLEC3B, the researchers analyzed data from the GEO, TCGA and Oncomine databases and validated the results using real-time PCR (15 patient samples) and immunohistochemistry (34 patient samples). The study found that CLEC3B is significantly downregulated in lung cancer, especially in early stage (IA) patients (p < 0.001). It demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy and was associated with poor progression-free survival and overall survival. Multivariate analysis further confirmed CLEC3B as an independent risk factor for disease-free survival. In addition, CLEC3B was associated with immune infiltration and activation, particularly in lung squamous cell carcinoma.
These findings suggest that CLEC3B is a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for lung cancer and may serve as an immune-related therapeutic target.
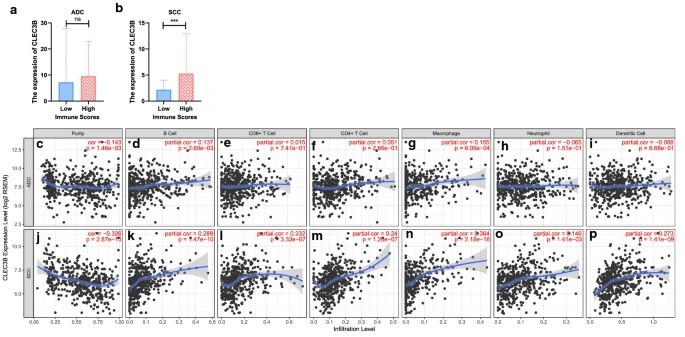 Figure 2. Correlation of CLEC3B expression with
immune infiltration level in ADC and SCC. a, b Comparison of CLEC3B expression between the high and low immune score groups of ADC and SCC. c–p CLEC3B is
related to tumor purity and immune infiltration levels of ADC and SCC by TIMER analysis. ADC, adenocarcinoma; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; ns, no
significance. ***p < 0.0. (Sun et al., 2020)
Figure 2. Correlation of CLEC3B expression with
immune infiltration level in ADC and SCC. a, b Comparison of CLEC3B expression between the high and low immune score groups of ADC and SCC. c–p CLEC3B is
related to tumor purity and immune infiltration levels of ADC and SCC by TIMER analysis. ADC, adenocarcinoma; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; ns, no
significance. ***p < 0.0. (Sun et al., 2020)
Macular degeneration is the leading cause of blindness worldwide, and this study aimed to identify a new subtype of macular-retinal dystrophy and its genetic predisposition in five families. The study identified a pathogenic CLEC3B variant in five multigenerational families diagnosed with autosomal dominant maculoretinopathy and implicated tetranectin, a plasminogen kringle-4 binding protein, in disease progression. Mice injected with the CLEC3B variant exhibited subretinal hyperreflective deposits, reduced retinal thickness, and diminished electroretinographic responses, while optokinetic tracking revealed significantly impaired spatial frequency, indicating visual dysfunction. These findings establish a new subtype of macular-retinal dystrophy associated with CLEC3B and provide new insights into the genetic basis of maculoretinopathy.
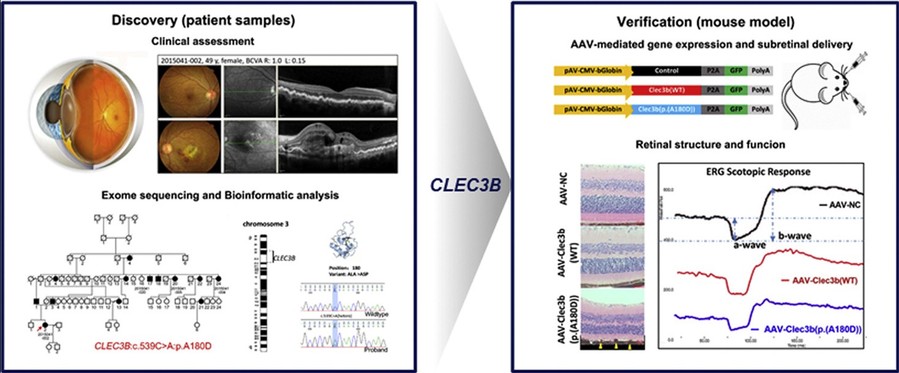 Figure 3. CLEC3B is a novel causative gene for
macular-retinal dystrophy (Zhou et al., 2022)
Figure 3. CLEC3B is a novel causative gene for
macular-retinal dystrophy (Zhou et al., 2022)
Several therapeutic proteins have been explored for targeting CLEC3B or its associated pathways:
With CLEC3B emerging as a potential biomarker and drug target, ongoing research is focused on developing targeted therapies that exploit its role in fibrinolysis, cancer progression and immune regulation. Advances in monoclonal antibody therapy, recombinant protein engineering, and small molecule inhibitors hold promise for translating CLEC3B-targeted approaches into clinical practice.
Creative BioMart specializes in providing therapeutic proteins, explore our extensive product categories or contact us with any inquiries.
References
For more information on how our products could help advance your project, please contact us.
ENTER YOUR EMAIL HERE TO SUBSCRIBE.
Copyright © 2026 Creative BioMart. All Rights Reserved.