| Catalog# | Product Name | Size | Price | Qty | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THP-0020 | Tenecteplase; Modified Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) | 100ug | $798.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order |
| 500ug | $2,498.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order | ||
| 1mg | $3,998.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order | ||
| THP-0193 | Mirococept, Human Complement Receptor 1 (CR1) | 1 vial | $3,998.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order |
Complement C3 (C3) plays a central role in the complement system, a critical component of innate immunity. As the convergence point of all three complement pathways, C3 is implicated in several inflammatory and immune-mediated diseases, making it an attractive drug target. In recent years, therapeutic strategies targeting C3 have been developed to attenuate excessive complement activation in diseases such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS).
NCBI Gene ID: 718
UniProtKB ID: P01024
C3 is primarily synthesized in the liver and circulates as an inactive precursor. Upon activation by C3 convertases (C4b2a in the classical/lectin pathway and C3bBb in the alternative pathway), C3 is cleaved into C3a and C3b. C3a functions as an anaphylatoxin, promoting inflammation through mast cell degranulation and leukocyte recruitment, whereas C3b functions as an opsonin, facilitating phagocytosis and clearance of immune complexes. In addition, C3b amplifies complement activation by forming additional C3 convertases, resulting in a positive feedback loop that enhances the immune response.
The importance of C3 in immune defense is further emphasized by its ability to interact with complement receptors, which mediate various immunoregulatory functions. CR1 aids in the clearance of immune complexes and inhibits complement activation, while CR2 plays a role in B cell activation and adaptive immunity. CR3 and CR4 contribute to phagocytosis and immune cell adhesion, further emphasizing the role of C3 in orchestrating immune responses. In addition, C3 degradation products such as iC3b and C3dg contribute to immune modulation by dampening excessive inflammation and promoting immune tolerance.
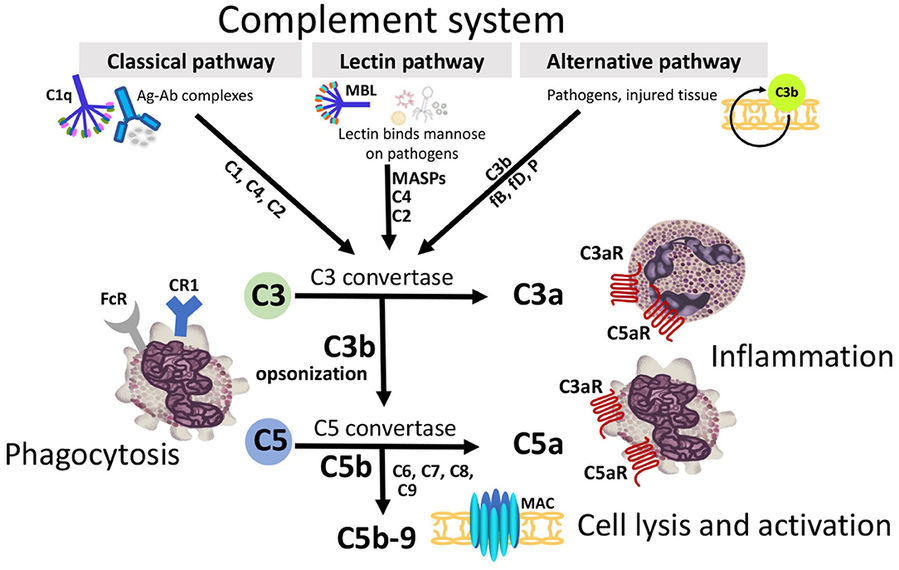 Figure 1. Three extracellular complement initiation
pathways culminate in a common terminal pathway. (Girardi et al., 2020)
Figure 1. Three extracellular complement initiation
pathways culminate in a common terminal pathway. (Girardi et al., 2020)
Due to its central role in complement activation, C3 dysregulation is implicated in numerous pathological conditions:
Targeting C3 Given its central role in complement activation, C3 inhibition represents a promising therapeutic approach. Several strategies have been developed to target C3 directly or modulate its activation pathways.
| Small Molecule and Peptide Inhibitors | Compstatin and Pegcetacoplan | Compstatin-derived inhibitors bind to C3 and prevent its cleavage, thereby halting complement activation. Pegcetacoplan, an FDA-approved drug, is used for treating PNH by reducing extravascular hemolysis. |
| Monoclonal Antibodies | Mirococept | A complement inhibitor currently under development for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and I/RI. |
| Regulatory Protein-Based Therapies | Soluble Complement Receptor 1 (sCR1) | A recombinant protein that enhances C3b degradation, reducing complement-mediated inflammation. |
| Factor H-based Therapies | Factor H mimetics are being explored for complement regulation in diseases such as C3G and aHUS. |
Creative BioMart provides a comprehensive range of high-quality therapeutic proteins. Contact us today to accelerate your research and therapeutic development!
Reference
For more information on how our products could help advance your project, please contact us.
ENTER YOUR EMAIL HERE TO SUBSCRIBE.
Copyright © 2026 Creative BioMart. All Rights Reserved.