| Catalog# | Product Name | Size | Price | Qty | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THP-0196 | Tagraxofusp | 1 vial | $3,998.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order |
ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 2 (ARL2) is a member of the ARF family of small GTP-binding proteins, which regulate intracellular trafficking, cytoskeletal dynamics, and mitochondrial homeostasis. ARL2 plays critical roles in cellular processes, including microtubule organization, protein transport, and energy metabolism. Dysregulation of ARL2 has been implicated in cancer progression, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders, making it a promising target for therapeutic development.
NCBI Gene ID: 402
UniProtKB ID: P36404
ARL2 is a small GTPase protein, structurally similar to the ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs). Like other members of the ARF family, ARL2 contains a GTP-binding domain that facilitates its role in regulating cellular processes. This domain binds to guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and undergoes conformational changes in response to GTP binding and hydrolysis, enabling ARL2 to interact with various effector proteins.
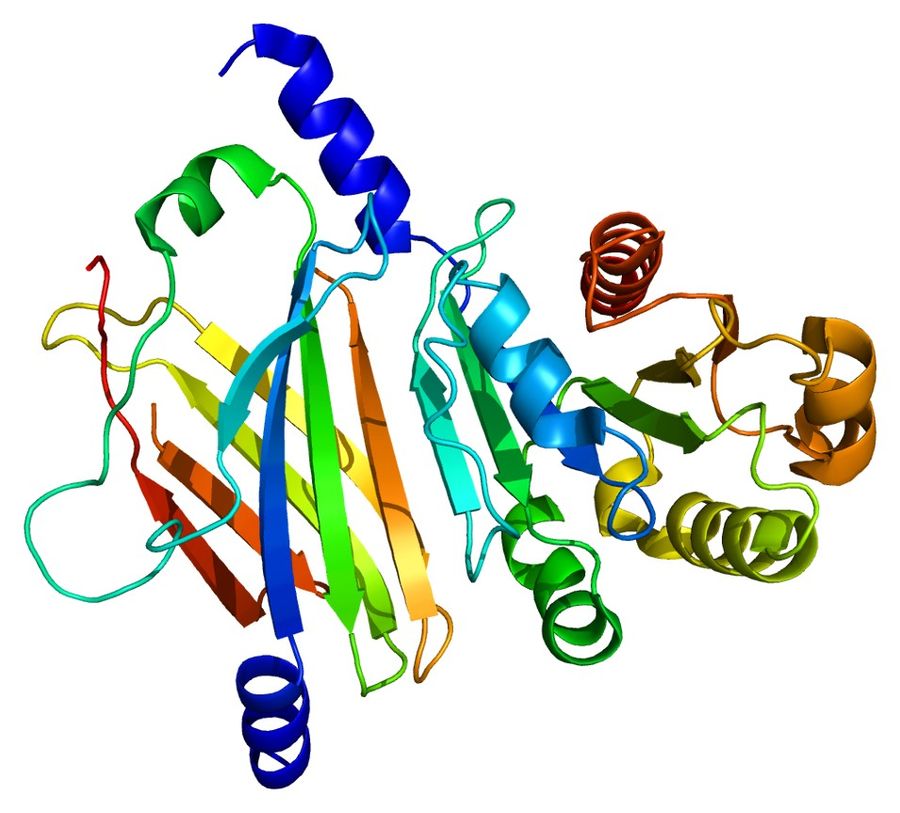 Figure 1. Structure of the ARL2 protein, PDB
code: 1KSG.
Figure 1. Structure of the ARL2 protein, PDB
code: 1KSG.
ARL2 is primarily located in the cytoplasm where it plays a critical role in the regulation of various cellular activities. Its cellular distribution and function are influenced by its ability to interact with different compartments and cellular machinery:
Small GTP-binding protein that cycles between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound form, the rate of cycling being regulated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF) and GTPase-activating proteins (GAP). Its key functions include:
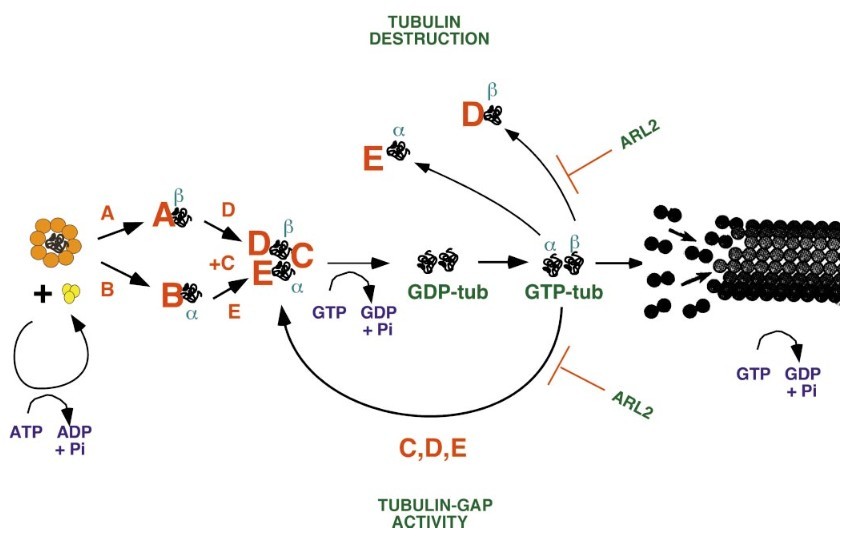 Figure 2. Model depicting the action of Arl2 in
the reactions involved in the assembly of the tubulin heterodimer and modulation of its guanine nucleotide state. The chaperonin CCT is shown in orange,
prefoldin/GimC is in yellow, and cofactors are denoted by red letters. (Bhamidipati et al., 2000)
Figure 2. Model depicting the action of Arl2 in
the reactions involved in the assembly of the tubulin heterodimer and modulation of its guanine nucleotide state. The chaperonin CCT is shown in orange,
prefoldin/GimC is in yellow, and cofactors are denoted by red letters. (Bhamidipati et al., 2000)
Aberrant ARL2 expression or function has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several diseases:
Therapeutic strategies targeting ARL2 aim to modulate its activity, either by inhibiting its function in overactive pathways (such as in cancer) or by restoring its activity in conditions where it is downregulated or dysfunctional (like in neurodegeneration).
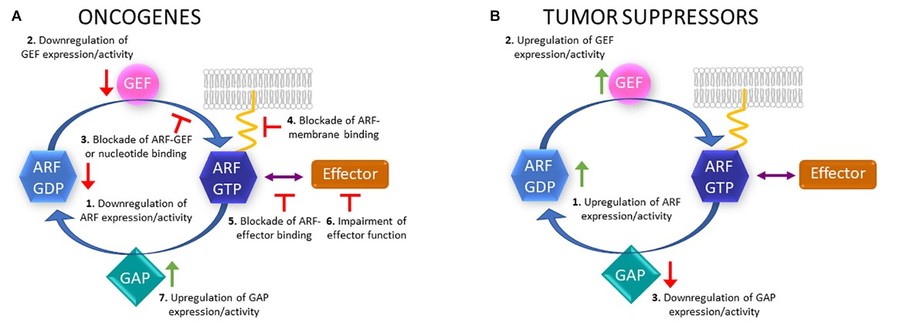 Figure 3. Putative therapeutic strategies to
target ARF proteins, GEFs, GAPs and effectors. (A) In the case of ARF family members that can act as oncogenes, their expression or activity could be
downregulated (1); GEF activity or expression downregulated (2); ARF-GEF binding blocked or nucleotide binding blocked (3); active ARF binding to membranes
(4) or effectors blocked (5); effector function impaired (6); GAP expression or activity upregulated (7). (B) Regarding ARF proteins that can act as tumor
suppressors, their expression or activity could be upregulated (1); GEF activity or expression upregulated (2); GAP activity or expression downregulated
(3). (Casalou et al., 2020)
Figure 3. Putative therapeutic strategies to
target ARF proteins, GEFs, GAPs and effectors. (A) In the case of ARF family members that can act as oncogenes, their expression or activity could be
downregulated (1); GEF activity or expression downregulated (2); ARF-GEF binding blocked or nucleotide binding blocked (3); active ARF binding to membranes
(4) or effectors blocked (5); effector function impaired (6); GAP expression or activity upregulated (7). (B) Regarding ARF proteins that can act as tumor
suppressors, their expression or activity could be upregulated (1); GEF activity or expression upregulated (2); GAP activity or expression downregulated
(3). (Casalou et al., 2020)
While direct drug targeting of ARL2 remains an evolving field, small molecules, peptides and biologics designed to modulate ARL2 activity are under investigation. These drugs focus on altering the binding affinity of ARL2 to its partners or inhibiting its GTPase activity, with the goal of influencing cellular processes associated with disease. For example, targeting ARL2 in cancer therapy could disrupt tumor cell migration or enhance the efficacy of existing treatments. In neurological diseases, correcting ARL2 activity could restore cellular homeostasis and slow disease progression.
Research into drugs that specifically target ARL2 is still in its early stages, but it holds promising therapeutic potential for treating a range of disorders by modulating the protein's activity and restoring normal cellular functions.
Creative BioMart is a trusted supplier of therapeutic proteins with comprehensive categories. Contact us with any questions to learn more!
References
For more information on how our products could help advance your project, please contact us.
ENTER YOUR EMAIL HERE TO SUBSCRIBE.
Copyright © 2026 Creative BioMart. All Rights Reserved.