Calreticulin (encoded by the gene CALR) is a multifunctional, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone protein involved in calcium homeostasis,
glycoprotein folding, and immune modulation. Beyond its ER-related functions, calreticulin has been implicated in various pathophysiological conditions,
including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and cardiovascular disorders. In particular, mutations in the calreticulin gene are recognized as key drivers in
myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), making it an attractive target for therapeutic intervention.
NCBI Gene ID: 811
UniProtKB ID: P27797
Structure of Calreticulin
Calreticulin is a highly conserved protein primarily localized in the ER but also found on the cell surface and in extracellular environments. It consists
of three distinct domains:
- N-terminal domain: Contains a signal peptide and is responsible for substrate recognition in glycoprotein folding.
- Proline-rich P-domain: Interacts with other ER chaperones, such as calnexin and ERp57, for protein quality control.
- C-terminal domain: Binds calcium with high capacity and regulates calcium-dependent signaling pathways.
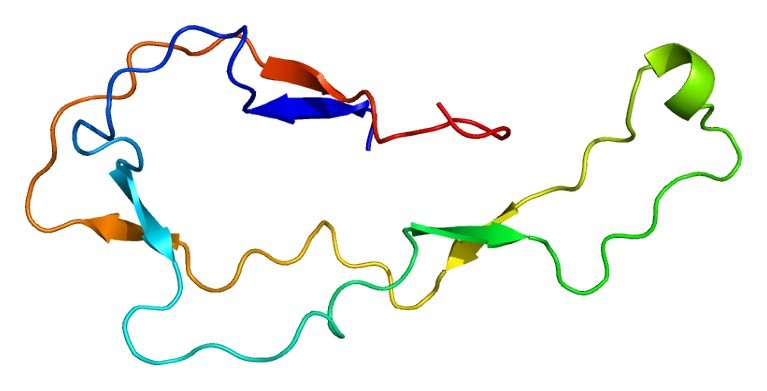 Figure 1. Structure of the CALR protein, PDB code:
1HHN.
Figure 1. Structure of the CALR protein, PDB code:
1HHN.
Functions of Calreticulin
-
Role in Protein Folding and Quality Control: Calreticulin is an essential component of the calnexin-calreticulin cycle, which ensures
proper folding of glycoproteins prior to their transport to the Golgi apparatus. It binds misfolded proteins and prevents their aggregation, thereby
promoting ER-associated degradation (ERAD). Dysfunction in this process contributes to diseases such as neurodegeneration and cancer.
-
Role in Calcium Homeostasis: Calreticulin functions as a major calcium buffer within the ER, regulating intracellular calcium levels.
Calcium signaling is critical for several cellular processes, including apoptosis, immune responses and inflammation. Alterations in
calreticulin-mediated calcium regulation have been implicated in tumorigenesis and immune dysregulation.
-
Extracellular and Cell-Surface Functions: Although calreticulin is predominantly an ER protein, it is also translocated to the cell
surface, where it plays a role in immunogenic cell death (ICD). Surface-exposed calreticulin (ecto-CRT) acts as an "eat-me" signal, promoting the
phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by dendritic cells and macrophages. This function is particularly relevant in cancer immunotherapy.
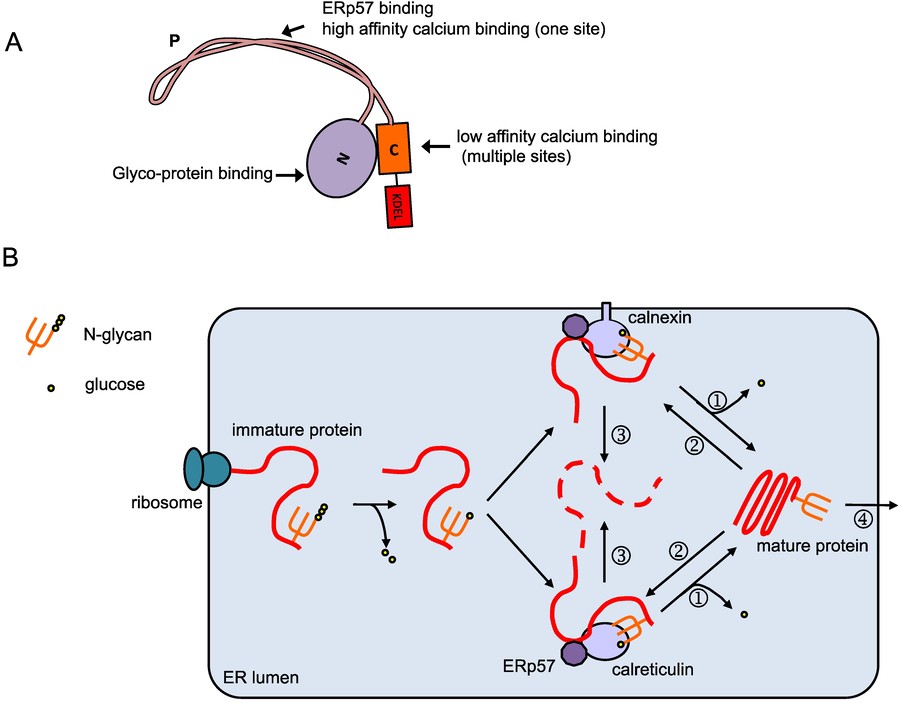 Figure 2. Overview of the calreticulin protein and
its function. (A) Domain organization of calreticulin. The calreticulin protein contains the N-terminal signal peptide, N-domain, P-domain,
C-domain and the ER-retention signal KDEL. The N- and P- domain are responsible for the chaperone function, while the C-domain is mainly responsible for
calcium binding; (B) Calreticulin/calnexin cycle. Native protein peptides being synthesized on the rough ER translocate into the ER lumen
and are glycosylated. The glycosylated protein is then modified by glucosidases I and II, and binds to calreticulin and/or calnexin. The oxidoreductase
ERp57 associates with calreticulin and calnexin, and catalyzes the formation and breakage of protein disulfide bonds to assist folding. When folding is
completed, glucosidases II further trims the glycan () and the glycoprotein is released from calreticulin/calnexin and transported out of the ER (1).
Incompletely-folded proteins are re-glucosylated by UGGT (UDP-glucose:glycoprotein transferase, 2), and remain bound to calreticulin/calnexin to continue
folding. Prolonged interaction with calreticulin/calnexin targets the proteins to ERAD (ER-associated degradation, 3). (Jiang et al., 2014)
Figure 2. Overview of the calreticulin protein and
its function. (A) Domain organization of calreticulin. The calreticulin protein contains the N-terminal signal peptide, N-domain, P-domain,
C-domain and the ER-retention signal KDEL. The N- and P- domain are responsible for the chaperone function, while the C-domain is mainly responsible for
calcium binding; (B) Calreticulin/calnexin cycle. Native protein peptides being synthesized on the rough ER translocate into the ER lumen
and are glycosylated. The glycosylated protein is then modified by glucosidases I and II, and binds to calreticulin and/or calnexin. The oxidoreductase
ERp57 associates with calreticulin and calnexin, and catalyzes the formation and breakage of protein disulfide bonds to assist folding. When folding is
completed, glucosidases II further trims the glycan () and the glycoprotein is released from calreticulin/calnexin and transported out of the ER (1).
Incompletely-folded proteins are re-glucosylated by UGGT (UDP-glucose:glycoprotein transferase, 2), and remain bound to calreticulin/calnexin to continue
folding. Prolonged interaction with calreticulin/calnexin targets the proteins to ERAD (ER-associated degradation, 3). (Jiang et al., 2014)
CALR in Disease Pathogenesis
-
CALR Mutations in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs): Somatic mutations in CALR are major drivers of essential
thrombocythemia (ET) and primary myelofibrosis (PMF), two types of MPNs. These mutations generate a novel C-terminal sequence that disrupts calcium
homeostasis and alters cytokine signaling, particularly via the thrombopoietin receptor (MPL). The oncogenic potential of mutant CALR (mut-CALR) is
linked to its ability to activate JAK-STAT signaling, promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation.
-
CALR and Cancer: In addition to MPNs, altered CALR expression has been observed in solid tumors, including breast,
lung, and ovarian cancers. Overexpression of CALR has been associated with tumor immune evasion, chemoresistance, and metastasis. Conversely,
ecto-CRT enhances the immunogenicity of dying cancer cells, making it a potential target for immunotherapy.
-
Calreticulin in Autoimmune Diseases: Calreticulin has been implicated in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It may act as an autoantigen, triggering aberrant immune responses. Targeting calreticulin may provide therapeutic
benefits by modulating its role in immune activation.
-
Calreticulin in Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Calreticulin's role in calcium homeostasis makes it relevant to
cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure and atherosclerosis. In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, calreticulin
dysregulation contributes to ER stress, protein misfolding and neuronal death.
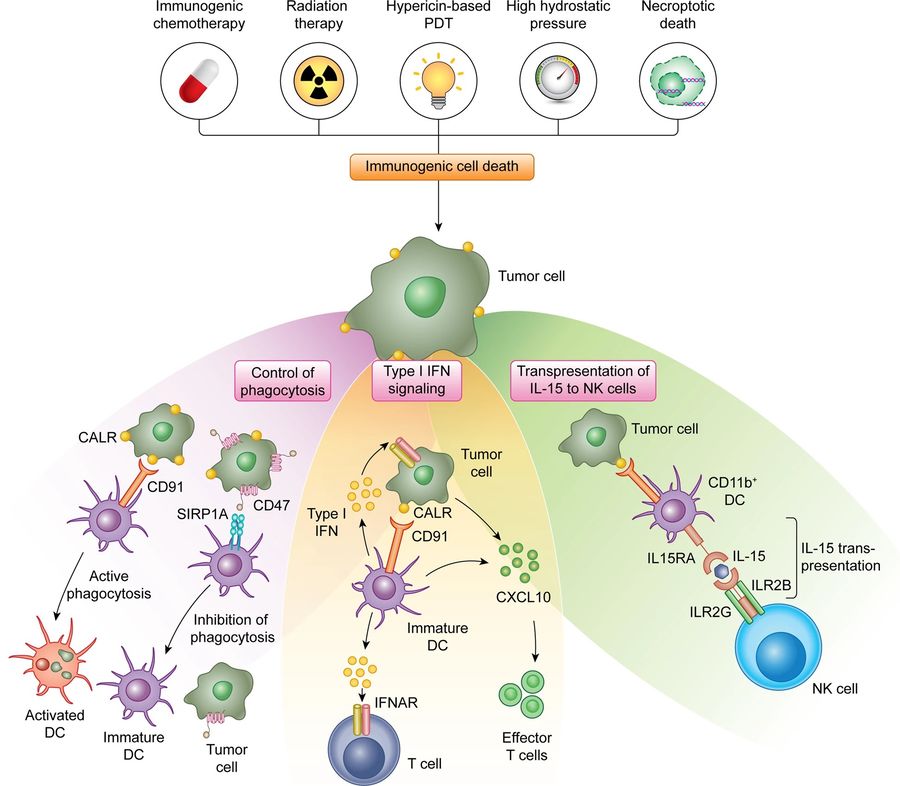 Figure 3. The exposure of CALR on the surface of
stressed and dying tumor cells mediate multipronged immunostimulatory effect. First, surface-exposed CALR promotes the uptake of dying cells or their
corpses by DCs, a process that is actively inhibited by CD47. Second, the exposure of CALR has been associated with the activation of an IFN response in
dying cells, although the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Third, surface-exposed CALR promotes the expansion of CD11b+CD14+
monocytes that proficiently trans-present IL15 to NK cells. CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; IL2RB, interleukin 2 receptor subunit beta;
IL2RG, interleukin 2 receptor subunit gamma; PDT, photodynamic therapy; SIRP1A, signal regulatory protein alpha. (Fucikova et al., 2021)
Figure 3. The exposure of CALR on the surface of
stressed and dying tumor cells mediate multipronged immunostimulatory effect. First, surface-exposed CALR promotes the uptake of dying cells or their
corpses by DCs, a process that is actively inhibited by CD47. Second, the exposure of CALR has been associated with the activation of an IFN response in
dying cells, although the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Third, surface-exposed CALR promotes the expansion of CD11b+CD14+
monocytes that proficiently trans-present IL15 to NK cells. CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; IL2RB, interleukin 2 receptor subunit beta;
IL2RG, interleukin 2 receptor subunit gamma; PDT, photodynamic therapy; SIRP1A, signal regulatory protein alpha. (Fucikova et al., 2021)
Therapeutic Strategies Targeting CALR
-
Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs): Monoclonal antibodies have been developed to specifically target mutant CALR in diseases like MPNs. These
antibodies can bind to the unique neoepitope present in mutant CALR, allowing for selective targeting of mutated cells without affecting normal
CALR-expressing cells. This approach has the potential to be highly specific and reduce off-target effects.
-
Cytokine-Based Therapies: Because calreticulin is involved in cytokine signaling, therapeutic proteins that affect calreticulin's
interaction with cytokine receptors could modulate immune responses. In MPNs, targeting calreticulin's activation of the JAK-STAT pathway with JAK
inhibitors has been effective in slowing disease progression. Similarly, engineered cytokines or receptor blockers could be developed to alter
calreticulin-driven pathways in autoimmune diseases or cancer.
-
Fusion Proteins and Peptides: Fusion proteins or peptides designed to disrupt the interaction between calreticulin and other cellular
components, such as the thrombopoietin receptor (MPL) in MPNs, could selectively inhibit the oncogenic effects of mutant calreticulin. By designing
fusion proteins that block calreticulin's binding sites, it's possible to prevent abnormal signaling that drives malignancy or inflammation.
-
Immunotherapy Approaches: The role of calreticulin in the immune recognition of tumors can be exploited through immunotherapy.
Therapeutic proteins that increase calreticulin exposure on the surface of cancer cells could enhance the immune system's ability to recognize and
attack tumors. For example, certain chemotherapeutic agents or molecular activators can induce calreticulin exposure, making the tumor more susceptible
to immune attack. These therapies may be combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors to further enhance the immune response.
Recombinant Human F8/Antihemophilic Factor
-
Moroctocog Alfa: Moroctocog alfa is a recombinant human coagulation factor VIII (rFVIII) used to treat hemophilia A. Hemophilia A is a genetic disorder caused by a
deficiency in Factor VIII, a critical protein in the blood clotting cascade. Moroctocog alfa replaces the missing or deficient Factor VIII in
individuals with hemophilia A, helping to prevent or control bleeding episodes.
-
Lonoctocog Alfa: Lonoctocog alfa is another recombinant Factor VIII therapy used in the treatment of hemophilia A. Lonoctocog alfa is a modified form of recombinant
human Factor VIII with a prolonged half-life due to its specific structural modifications. The modifications allow it to circulate in the bloodstream
for a longer period of time, reducing the frequency of dosing required for hemophilia patients.
Creative BioMart, your source for therapeutic proteins, offers
recombinant human F8/antihemophilic factor targeting calreticulin.
Contact us to learn more!
References
- Fucikova J, Spisek R, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Calreticulin and cancer. Cell Res. 2021;31(1):5-16. doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0383-9
-
Jiang Y, Dey S, Matsunami H. Calreticulin: roles in cell-surface protein expression. Membranes. 2014;4(3):630-641. doi:10.3390/membranes4030630
 Figure 1. Structure of the CALR protein, PDB code:
1HHN.
Figure 1. Structure of the CALR protein, PDB code:
1HHN.
 Figure 2. Overview of the calreticulin protein and
its function. (A) Domain organization of calreticulin. The calreticulin protein contains the N-terminal signal peptide, N-domain, P-domain,
C-domain and the ER-retention signal KDEL. The N- and P- domain are responsible for the chaperone function, while the C-domain is mainly responsible for
calcium binding; (B) Calreticulin/calnexin cycle. Native protein peptides being synthesized on the rough ER translocate into the ER lumen
and are glycosylated. The glycosylated protein is then modified by glucosidases I and II, and binds to calreticulin and/or calnexin. The oxidoreductase
ERp57 associates with calreticulin and calnexin, and catalyzes the formation and breakage of protein disulfide bonds to assist folding. When folding is
completed, glucosidases II further trims the glycan () and the glycoprotein is released from calreticulin/calnexin and transported out of the ER (1).
Incompletely-folded proteins are re-glucosylated by UGGT (UDP-glucose:glycoprotein transferase, 2), and remain bound to calreticulin/calnexin to continue
folding. Prolonged interaction with calreticulin/calnexin targets the proteins to ERAD (ER-associated degradation, 3). (Jiang et al., 2014)
Figure 2. Overview of the calreticulin protein and
its function. (A) Domain organization of calreticulin. The calreticulin protein contains the N-terminal signal peptide, N-domain, P-domain,
C-domain and the ER-retention signal KDEL. The N- and P- domain are responsible for the chaperone function, while the C-domain is mainly responsible for
calcium binding; (B) Calreticulin/calnexin cycle. Native protein peptides being synthesized on the rough ER translocate into the ER lumen
and are glycosylated. The glycosylated protein is then modified by glucosidases I and II, and binds to calreticulin and/or calnexin. The oxidoreductase
ERp57 associates with calreticulin and calnexin, and catalyzes the formation and breakage of protein disulfide bonds to assist folding. When folding is
completed, glucosidases II further trims the glycan () and the glycoprotein is released from calreticulin/calnexin and transported out of the ER (1).
Incompletely-folded proteins are re-glucosylated by UGGT (UDP-glucose:glycoprotein transferase, 2), and remain bound to calreticulin/calnexin to continue
folding. Prolonged interaction with calreticulin/calnexin targets the proteins to ERAD (ER-associated degradation, 3). (Jiang et al., 2014)
 Figure 3. The exposure of CALR on the surface of
stressed and dying tumor cells mediate multipronged immunostimulatory effect. First, surface-exposed CALR promotes the uptake of dying cells or their
corpses by DCs, a process that is actively inhibited by CD47. Second, the exposure of CALR has been associated with the activation of an IFN response in
dying cells, although the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Third, surface-exposed CALR promotes the expansion of CD11b+CD14+
monocytes that proficiently trans-present IL15 to NK cells. CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; IL2RB, interleukin 2 receptor subunit beta;
IL2RG, interleukin 2 receptor subunit gamma; PDT, photodynamic therapy; SIRP1A, signal regulatory protein alpha. (Fucikova et al., 2021)
Figure 3. The exposure of CALR on the surface of
stressed and dying tumor cells mediate multipronged immunostimulatory effect. First, surface-exposed CALR promotes the uptake of dying cells or their
corpses by DCs, a process that is actively inhibited by CD47. Second, the exposure of CALR has been associated with the activation of an IFN response in
dying cells, although the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Third, surface-exposed CALR promotes the expansion of CD11b+CD14+
monocytes that proficiently trans-present IL15 to NK cells. CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; IL2RB, interleukin 2 receptor subunit beta;
IL2RG, interleukin 2 receptor subunit gamma; PDT, photodynamic therapy; SIRP1A, signal regulatory protein alpha. (Fucikova et al., 2021)