| Catalog# | Product Name | Size | Price | Qty | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THP-0303 | Nepidermin, Recombinant human epidermal growth factor (rhEGF) | 1 vial | $3,998.00 |
|
Add to Cart Order |
Hair is considered an accessory structure of the ectoderm along with sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails. Hair loss is a disease of aging hair follicles due to endogenous factors such as aging and hormones, as well as exogenous factors such as stress and environmental hormones. Hair loss is not usually life-threatening, but the number of patients suffering from hair loss continues to increase. Also, hair loss can affect social interactions and the psychological well-being of the patient.
Hair follicle morphogenesis requires intricately controlled regulation of apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation. The hair follicle is a microscopic organ that undergoes anagen, regression, and resting phases during its postnatal life cycle. Once hair loss begins, it is progressive and irreversible, and there is no radical treatment for hair loss.
A variety of cytokines and growth factors are involved in the regulation of hair morphogenesis and the hair growth cycle. Treatment options used to date include stimulating existing hair follicles to make new hair grow faster and more abundant or transplanting new hair. Another option is the use of cell therapy, where adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) and their conditioned medium (CM) have been reported to have hair growth effects, but results have been largely unsatisfactory to date.
Epidermal growth factor (EGF), the first growth factor discovered, is a class of peptide substances widely present in mammals and plays an important role in regulating cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation. Epithelial regulatory proteins (EREG) are members of the EGF family and play a role in inflammation, wound healing, normal physiology, and malignancy. In addition to this, human EREG (hEREG) has been reported to induce hair shaft elongation to stimulate keratin-forming cells. The hair-inducing effects of EREG have also been investigated and the results showed that EREG significantly promotes hair growth, therefore, EREG therapy may provide a new solution for hair loss treatment.
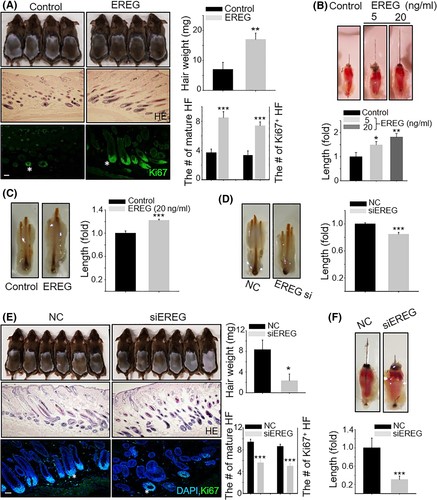
Figure1. EREG promotes hair growth in vivo and ex vivo . (Choi, N. K., et al. , 2020)
Human EGF (hEGF) exerts its physiological effects by binding to hEGF receptors on cell membranes, and with advances in biotechnology, large-scale production of recombinant human epidermal growth factor (rhEGF) is possible, and many formulations have been developed for the healing of chronic wounds, burns, and diabetic foot ulcers. Recently, rhEGF has even been used for cosmetic purposes.
Creative BioMart is focusing on the use of EGF in clinical therapy (strong pro-division effects on a variety of tissue cells) and in a medical aesthetic direction (a potential new way to treat hair loss). We continue to provide researchers with rhEGF to explore further possibilities to expand its role from the clinical to the medical aesthetic field. If you need more recombinant protein products related to hair loss research and treatment, please contact our staff directly who will provide you with an updated product list and detailed product solutions.
Reference
For more information on how our products could help advance your project, please contact us.
ENTER YOUR EMAIL HERE TO SUBSCRIBE.
Copyright © 2026 Creative BioMart. All Rights Reserved.